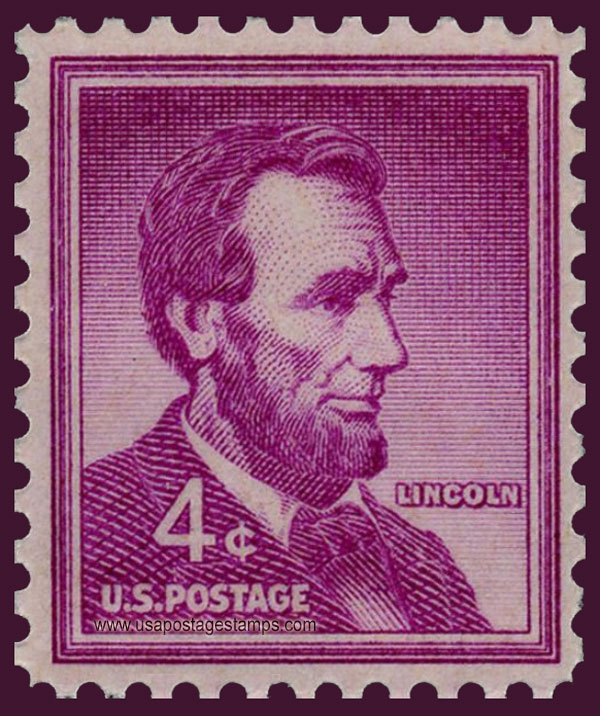
US 1954 Abraham Lincoln (1809-1865) 4c. Scott. 1036

Series: Liberty Issue
Stamp details: Abraham Lincoln (1809-1865), 16th President of the U.S.A.
Issued date: 19-11-1954 (dd/mm/yyyy)
Face value: 4c.
Emission: Definitive
Watermark: No Watermark
Catalogue No:-
Scott (USA): 1036
Stanley Gibbons (UK): 1034
Michel (Germany): 657A
Yvert et Tellier (France): 589
Unificato (Italy): 824
Dimensions (height x width):
25.4mm x 22.2mm
Printer: Bureau of Engraving and Printing
Print Method: Rotary Press
Stamp Colors: Red violet
Perforation: Perf 11 x 10˝
Paper: Normal
Themes: Famous People, Head of State, Statesman, Politician, Antiracism
Note: Dry printing.
Stamp details: Abraham Lincoln (1809-1865), 16th President of the U.S.A.
Issued date: 19-11-1954 (dd/mm/yyyy)
Face value: 4c.
Emission: Definitive
Watermark: No Watermark
Catalogue No:-
Scott (USA): 1036
Stanley Gibbons (UK): 1034
Michel (Germany): 657A
Yvert et Tellier (France): 589
Unificato (Italy): 824
Dimensions (height x width):
25.4mm x 22.2mm
Printer: Bureau of Engraving and Printing
Print Method: Rotary Press
Stamp Colors: Red violet
Perforation: Perf 11 x 10˝
Paper: Normal
Themes: Famous People, Head of State, Statesman, Politician, Antiracism
Note: Dry printing.
Description:- Abraham Lincoln (1809-1865) was an American lawyer and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation through the American Civil War and succeeded in preserving the Union, abolishing slavery, bolstering the federal government, and modernizing the U.S. economy.
Lincoln was born into poverty in a log cabin in Kentucky and was raised on the frontier, primarily in Indiana. He was self-educated and became a lawyer, Whig Party leader, Illinois state legislator, and U.S. Congressman from Illinois. In 1849, he returned to his successful law practice in central Illinois. In 1854 he was angered by the Kansas–Nebraska Act that opened the territories to slavery, and re-entered politics. He soon became a leader of the new Republican Party. He reached a national audience in the 1858 Senate campaign debates against Stephen Douglas. Lincoln ran for President in 1860, sweeping the North to gain victory. Pro-slavery elements in the South viewed his election as a threat to slavery, and Southern states began seceding from the Union. During this time the newly formed Confederate States of America began seizing federal military bases in the south. Just over one month after Lincoln assumed the presidency, the Confederate States attacked Fort Sumter, a U.S. fort in South Carolina. Following the bombardment, Lincoln mobilized forces to suppress the rebellion and restore the Union.
Source: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abraham_Lincoln
Lincoln was born into poverty in a log cabin in Kentucky and was raised on the frontier, primarily in Indiana. He was self-educated and became a lawyer, Whig Party leader, Illinois state legislator, and U.S. Congressman from Illinois. In 1849, he returned to his successful law practice in central Illinois. In 1854 he was angered by the Kansas–Nebraska Act that opened the territories to slavery, and re-entered politics. He soon became a leader of the new Republican Party. He reached a national audience in the 1858 Senate campaign debates against Stephen Douglas. Lincoln ran for President in 1860, sweeping the North to gain victory. Pro-slavery elements in the South viewed his election as a threat to slavery, and Southern states began seceding from the Union. During this time the newly formed Confederate States of America began seizing federal military bases in the south. Just over one month after Lincoln assumed the presidency, the Confederate States attacked Fort Sumter, a U.S. fort in South Carolina. Following the bombardment, Lincoln mobilized forces to suppress the rebellion and restore the Union.
Source: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abraham_Lincoln